It is impossible to pass Juniper JN0-664 exam without any help in the short term. Come to Testking soon and find the most advanced, correct and guaranteed Juniper JN0-664 practice questions. You will get a surprising result by our Renew Service Provider - Professional (JNCIP-SP) practice guides.
Juniper JN0-664 Free Dumps Questions Online, Read and Test Now.
NEW QUESTION 1
Which two statements are correct about IS-IS interfaces? (Choose two.)
- A. If a broadcast interface is in both L1 and L2, one combined hello message is sent for both levels.
- B. If a point-to-point interface is in both L1 and L2, separate hello messages are sent for each level.
- C. If a point-to-point interface is in both L1 and L2, one combined hello message is sent for both levels.
- D. If a broadcast interface is in both L1 and L2, separate hello messages are sent for each level
Answer: BD
Explanation:
IS-IS supports two levels of routing: Level 1 (intra-area) and Level 2 (interarea). An IS-IS router can be either Level 1 only, Level 2 only, or both Level 1 and Level 2. A router that is both Level 1 and Level 2 is called a Level 1-2 router. A Level 1-2 router sends separate hello messages for each level on both point-to-point and broadcast interfaces1. A point-to-point interface provides a connection between a single source and a single destination. A broadcast interface behaves as if the router is connected to a LAN.
NEW QUESTION 2
Which three mechanisms are used by Junos platforms to evaluate incoming traffic for CoS purposes? (Choose three )
- A. rewrite rules
- B. behavior aggregate classifiers
- C. traffic shapers
- D. fixed classifiers
- E. multifield classifiers
Answer: BDE
Explanation:
Junos platforms use different mechanisms to evaluate incoming traffic for CoS purposes, such as:
✑ Behavior aggregate classifiers: These classifiers use a single field in a packet header to classify traffic into different forwarding classes and loss priorities based on predefined or user-defined values.
✑ Fixed classifiers: These classifiers use a fixed field in a packet header to classify traffic into different forwarding classes and loss priorities based on predefined values.
✑ Multifield classifiers: These classifiers use multiple fields in a packet header to classify traffic into different forwarding classes and loss priorities based on user- defined values and filters.
Rewrite rules and traffic shapers are not used to evaluate incoming traffic for CoS purposes, but rather to modify or shape outgoing traffic based on CoS policies.
NEW QUESTION 3
Which two statements are correct about VPLS tunnels? (Choose two.)
- A. LDP-signaled VPLS tunnels only support control bit 0.
- B. LDP-signaled VPLS tunnels use auto-discovery to provision sites
- C. BGP-signaled VPLS tunnels can use either RSVP or LDP between the PE routers.
- D. BGP-signaled VPLS tunnels require manual provisioning of sites.
Answer: BC
Explanation:
VPLS is a Layer 2 VPN technology that allows multiple sites to connect over a shared IP/MPLS network as if they were on the same LAN. VPLS tunnels can be signaled using either Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) or Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). LDP-signaled VPLS tunnels use auto-discovery to provision sites, meaning that PE routers can automatically discover other PE routers that belong to the same VPLS instance
NEW QUESTION 4
Exhibit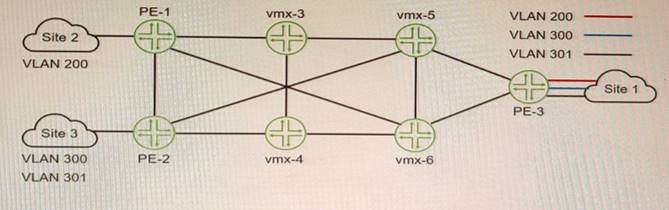
You want Site 1 to access three VLANs that are located in Site 2 and Site 3 The customer- facing interface on the PE-1 router is configured for Ethernet-VLAN encapsulation.
What is the minimum number of L2VPN routing instances to be configured to accomplish this task?
- A. 1
- B. 3
- C. 2
- D. 6
Answer: B
Explanation:
To allow Site 1 to access three VLANs that are located in Site 2 and Site 3, you need to configure three L2VPN routing instances on PE-1, one for each VLAN. Each L2VPN routing instance will have a different VLAN ID and a different VNI for VXLAN encapsulation. Each L2VPN routing instance will also have a different vrf-target export value to identify which VPN routes belong to which VLAN. This way, PE-1 can forward traffic from Site 1 to Site 2 and Site 3 based on the VLAN tags and VNIs.
NEW QUESTION 5
Exhibit
Which two statements about the configuration shown in the exhibit are correct? (Choose two.)
- A. This VPN connects customer sites that use different AS numbers.
- B. This VPN connects customer sites that use the same AS number
- C. A Layer 2 VPN is configured.
- D. A Layer 3 VPN is configured.
Answer: AD
Explanation:
The configuration shown in the exhibit is for a Layer 3 VPN that connects customer sites that use different AS numbers. A Layer 3 VPN is a type of VPN that uses MPLS labels to forward packets across a provider network and BGP to exchange routing information between PE routers and CE routers. A Layer 3 VPN allows customers to use different routing protocols and AS numbers at their sites, as long as they can peer with BGP at the PE-CE interface. In this example, CE-1 is using AS 65530 and CE-2 is using AS 65531, but they can still communicate through the VPN because they have BGP sessions with PE-1 and PE-2, respectively.
NEW QUESTION 6
Which origin code is preferred by BGP?
- A. Internal
- B. External
- C. Incomplete
- D. Null
Answer: C
Explanation:
BGP uses several attributes to select the best path for a destination prefix. One of these attributes is origin, which indicates how BGP learned about a route. The origin attribute can have one of three values: IGP, EGP, or Incomplete. IGP means that the route was originated by a network or aggregate statement within BGP or by redistribution from an IGP into BGP. EGP means that the route was learned from an external BGP peer (this value is obsolete since BGP version 4). Incomplete means that the route was learned by some other means, such as redistribution from a static route into BGP. BGP prefers routes with lower origin values, so Incomplete is preferred over EGP, which is preferred over IGP.
NEW QUESTION 7
Exhibit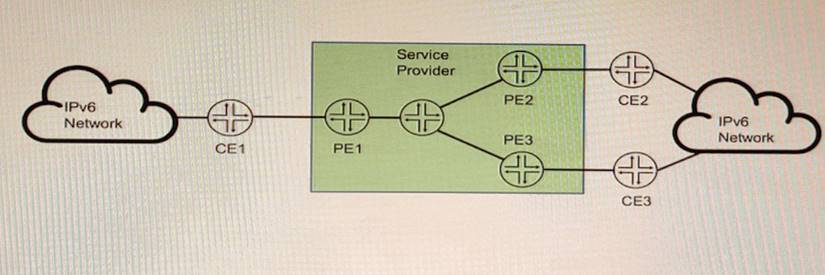
You are running a service provider network and must transport a customer's IPv6 traffic across your IPv4-based MPLS network using BGP You have already configured mpis ipv6- tunneling on your PE routers.
Which two statements are correct about the BGP configuration in this scenario? (Choose two.)
- A. You must configure family inet6 labcled-unicast between PE routers.
- B. You must configure family inet6 unicaat between PE and CE routers.
- C. You must configure family inet6 add-path between PE and CE routers.
- D. You must configure family inet6 unicast between PE routers
Answer: AB
Explanation:
To transport IPv6 traffic over an IPv4-based MPLS network using BGP, you need to configure two address families: family inet6 labeled-unicast and family inet6 unicast. The former is used to exchange IPv6 routes with MPLS labels between PE routers, and the latter is used to exchange IPv6 routes without labels between PE and CE routers. The mpis ipv6-tunneling command enables the PE routers to encapsulate the IPv6 packets with an MPLS label stack and an IPv4 header before sending them over the MPLS network.
NEW QUESTION 8
When building an interprovider VPN, you notice on the PE router that you have hidden routes which are received from your BGP peer with family inet labeled-unica3t configured.
Which parameter must you configure to solve this problem?
- A. Under the family inet labeled-unicast hierarchy, add the explicit null parameter.
- B. Under the protocols ospf hierarchy, add the traffic-engineering parameter.
- C. Under the family inet labeled-unicast hierarchy, add the resolve-vpn parameter.
- D. Under the protocols mpls hierarchy, add the traffic-engineering parameter
Answer: C
Explanation:
The resolve-vpn parameter is a BGP option that allows a router to resolve labeled VPN-IPv4 routes using unlabeled IPv4 routes received from another BGP peer with family inet labeled-unicast configured. This option enables interprovider VPNs without requiring MPLS labels between ASBRs or using VRF tables on ASBRs. In this scenario, you need to configure the resolve-vpn parameter under [edit protocols bgp group external family inet labeled-unicast] hierarchy level on both ASBRs.
NEW QUESTION 9
Exhibit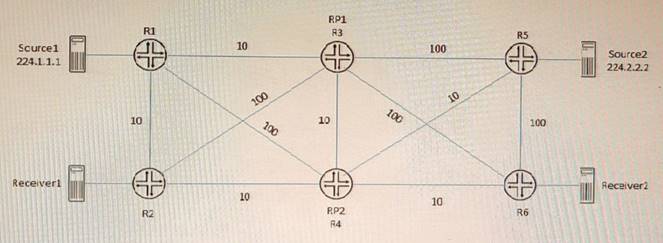
Referring to the exhibit, PIM-SM is configured on all routers, and Anycast-RP with Anycast- PIM is used for the discovery mechanism on RP1 and RP2. The interface metric values are shown for the OSPF area.
In this scenario, which two statements are correct about which RP is used? (Choose two.)
- A. Source2 will use RP2 and Received will use RP2 for group 224.2.2.2.
- B. Source2 will use RP1 and Receiver2 will use RP1 for group 224.2.2.2.
- C. Source1 will use RP1 and Receiver1 will use RP1 for group 224.1.1.1.
- D. Source1 will use RP1 and Receiver1 will use RP2 for group 224.1 1 1
Answer: AC
Explanation:
A sham link is a logical link between two PE routers that belong to the same OSPF area but are connected through an L3VPN. A sham link makes the PE routers appear as if they are directly connected, and prevents OSPF from preferring an intra-area back door link over the VPN backbone. A sham link creates an OSPF multihop neighborship between the PE routers using TCP port 646. The PEs exchange Type 1 OSPF LSAs instead of Type 3 OSPF LSAs for the L3VPN routes, which allows OSPF to use the correct metric for route selection1.
NEW QUESTION 10
Exhibit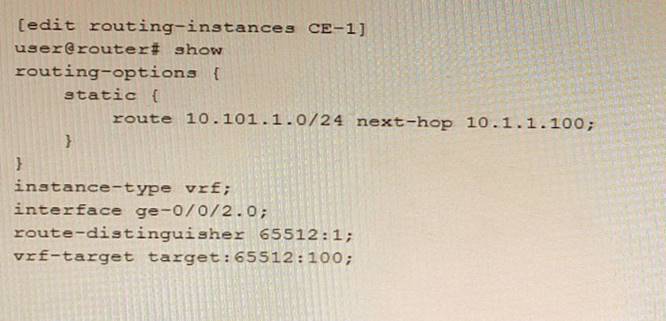
Referring to the exhibit, which statement is true?
- A. The 10.101.1.0/24 route will be shared if the vrf-table-label parameter is configured.
- B. The 10.101.1.0/24 route will only be shared if BGP is configured in the routing instance
- C. The 10.101.1 0/24 route will be shared if there are other VRFs that use the same route target community
- D. The 10.101.1.0/24 route will be shared if the auto-export parameter is configured
Answer: D
Explanation:
The auto-export parameter is a routing option that allows a routing instance to share routes with other routing instances or the master routing table. The auto-export parameter automatically exports routes from one routing instance to another based on the route target communities attached to the routes. In this scenario, the 10.101.1.0/24 route will be shared if the auto-export parameter is configured under [edit routing-options] hierarchy level.
NEW QUESTION 11
Exhibit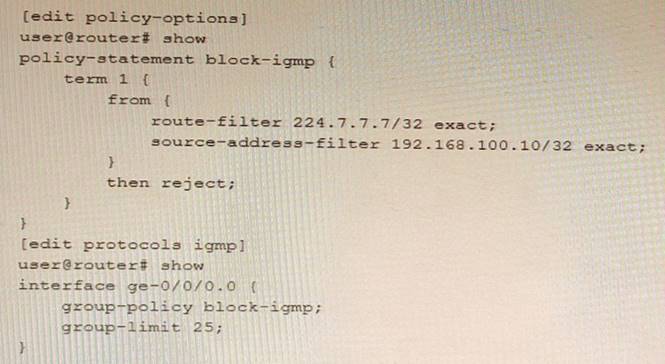
Based on the configuration contents shown in the exhibit, which statement is true?
- A. Joins for group 224.7.7.7 are rejected if the source address is 192.168.100.10
- B. Joins for any group are accepted if the group count value is less than 25.
- C. Joins for group 224.7.7.7 are always rejected, regardless of the group count.
- D. Joins for group 224.7.7.7 are accepted if the group count is less than 25
Answer: D
Explanation:
BGP policy framework is a set of tools that allows you to control the flow of routing information and apply routing policies based on various criteria. BGP policy framework consists of several components, such as route maps, prefix lists, community lists, AS path lists, and route filters. Route maps are used to define routing policies by matching certain conditions and applying certain actions. Prefix lists are used to filter routes based on their prefixes. Community lists are used to filter routes based on their community attributes. AS path lists are used to filter routes based on their AS path attributes. Route filters are used to filter routes based on their prefix length or range3. In this question, we have a route map named ISP-A that has two clauses: clause 10 and clause 20. Clause 10 matches any route with a prefix length between 8 and 24 bits and sets the local preference to 200. Clause 20 matches any route with a prefix of 224.7.7.7/32 and rejects it. The route map is applied inbound on the BGP neighborship with ISP-A. Based on this configuration, the correct statement is that joins for group 224.7.7.7 are always rejected, regardless of the group count. This is because clause 20 explicitly denies any route with a prefix of 224.7.7.7/32, which corresponds to the multicast group 224.7.7.7.
Reference: 3: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_bgp/configuration/xe-16/irg-xe-16-book/bgp-policy-framework.html
NEW QUESTION 12
Exhibit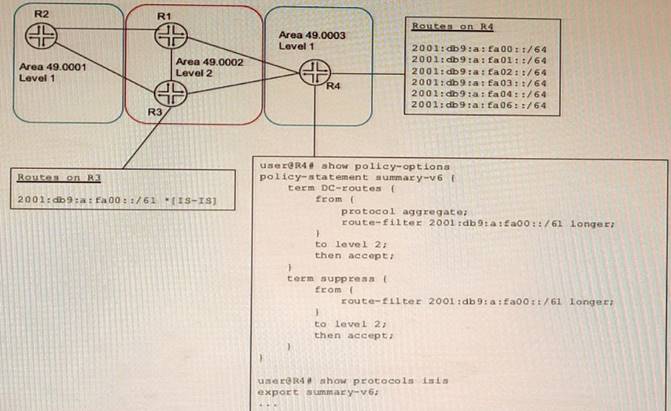
A network designer would like to create a summary route as shown in the exhibit, but the
configuration is not working.
Which three configuration changes will create a summary route? (Choose three.)
- A. set policy-options policy-statement leak-v6 term DC-routes then reject
- B. delete policy-options policy-statement leak-v6 term DC-routes from route-filter 2001: db9:a: fa00 : :/6l longer
- C. set policy—options policy-statement leak-v€ term DC—routes from route-filter 2001:db9:a:faOO::/61 exact
- D. delete protocols isis export summary-v6
- E. set protocols isis import summary-v6
Answer: BCD
Explanation:
To create a summary route for IS-IS, you need to configure a policy statement that matches the prefixes to be summarized and sets the next-hop to discard. You also need to configure a summary-address statement under the IS-IS protocol hierarchy that references the policy statement. In this case, the policy statement leak-v6 is trying to match the prefix 2001:db9:a:fa00::/61 exactly, but this prefix is not advertised by any router in the network. Therefore, no summary route is created. To fix this, you need to delete the longer keyword from the route-filter term and change the prefix length to /61 exact. This will match any prefix that falls within the /61 range. You also need to delete the export statement under protocols isis, because this will export all routes that match the policy statement to other IS-IS routers, which is not desired for a summary route.
NEW QUESTION 13
Exhibit
You want to use both links between R1 and R2 Because of the bandwidth difference between the two links, you must ensure that the links are used as much as possible.
Which action will accomplish this goal?
- A. Define a policy to tag routes with the appropriate bandwidth community.
- B. Disable multipath.
- C. Ensure that the metric-out parameter on the Gigabit Ethernet interface is higher than the 10 Gigibit Ethernet interface.
- D. Enable per-prefix load balancing.
Answer: D
Explanation:
VPLS is a Layer 2 VPN technology that allows multiple sites to connect over a shared IP/MPLS network as if they were on the same LAN. VPLS tunnels can be signaled using either Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) or Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). In this question, we have two links between R1 and R2 with different bandwidths (10 Gbps and 1 Gbps). We want to use both links as much as possible for VPLS traffic. To achieve this, we need to enable per-prefix load balancing on both routers. Per-prefix load balancing is a feature that allows a router to distribute traffic across multiple equal-cost or unequal- cost paths based on the destination prefix of each packet. This improves the utilization of multiple links and provides better load sharing than per-flow load balancing, which distributes traffic based on a hash of source and destination addresses4. Per-prefix load balancing can be enabled globally or per interface using the load-balance per-packet command.
Reference: 4: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/multiprotocol-label-switching-mpls/mpls/137544-technote-mpls-00.html
NEW QUESTION 14
Exhibit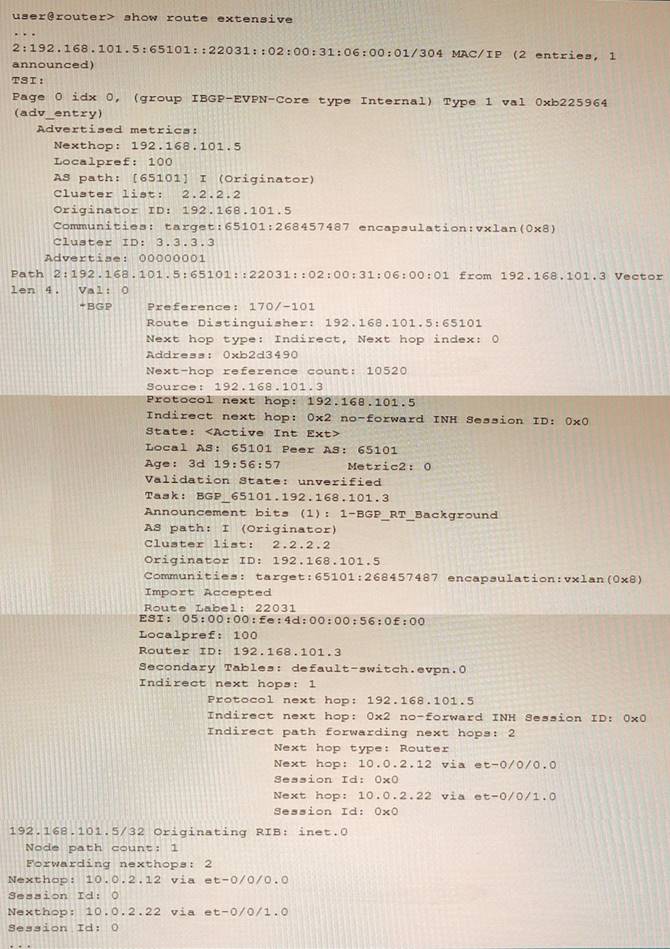
Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
- A. This route is learned through EBGP
- B. This is an EVPN Type-2 route.
- C. The device advertising this route into EVPN is 192.168.101.5.
- D. The devices advertising this route into EVPN are 10 0 2 12 and 10.0.2.22.
Answer: BC
Explanation:
This is an EVPN Type-2 route, also called a MAC/IP advertisement route, that is used to advertise host IP and MAC address information to other VTEPs in an EVPN network. The route type field in the EVPN NLRI has a value of 2, indicating a Type-2 route. The device advertising this route into EVPN is 192.168.101.5, which is the IP address of the VTEP that learned the host information from the local CE device. This IP address is carried in the MPLS label field of the route as part of the VXLAN encapsulation.
NEW QUESTION 15
You are configuring a BGP signaled Layer 2 VPN across your MPLS enabled core network. Your PE-2 device connects to two sites within the s VPN
In this scenario, which statement is correct?
- A. By default on PE-2, the site's local ID is automatically assigned a value of 0 and must be configured to match the total number of attached sites.
- B. You must create a unique Layer 2 VPN routing instance for each site on the PE-2 device.
- C. You must use separate physical interfaces to connect PE-2 to each site.
- D. By default on PE-2, the remote site IDs are automatically assigned based on the order that you add the interfaces to the site configuration.
Answer: D
Explanation:
BGP Layer 2 VPNs use BGP to distribute endpoint provisioning information and set up pseudowires between PE devices. BGP uses the Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) Routing Information Base (RIB) to store endpoint provisioning information, which is updated each time any Layer 2 virtual forwarding instance (VFI) is configured. The prefix and path information is stored in the L2VPN database, which allows BGP to make decisions about the best path.
In BGP Layer 2 VPNs, each site has a unique site ID that identifies it within a VFI. The site ID can be manually configured or automatically assigned by the PE device. By default, the site ID is automatically assigned based on the order that you add the interfaces to the site configuration. The first interface added to a site configuration has a site ID of 1, the second interface added has a site ID of 2, and so on.
Option D is correct because by default on PE-2, the remote site IDs are automatically assigned based on the order that you add the interfaces to the site configuration. Option A is not correct because by default on PE-2, the site’s local ID is automatically assigned a value of 0 and does not need to be configured to match the total number of attached sites. Option B is not correct because you do not need to create a unique Layer 2 VPN routing instance for each site on the PE-2 device. You can create one routing instance for all sites within a VFI. Option C is not correct because you do not need to use separate physical interfaces to connect PE-2 to each site. You can use subinterfaces or service instances on a single physical interface.
NEW QUESTION 16
......
100% Valid and Newest Version JN0-664 Questions & Answers shared by Thedumpscentre.com, Get Full Dumps HERE: https://www.thedumpscentre.com/JN0-664-dumps/ (New 65 Q&As)